JavaDoc Coverage Doclet
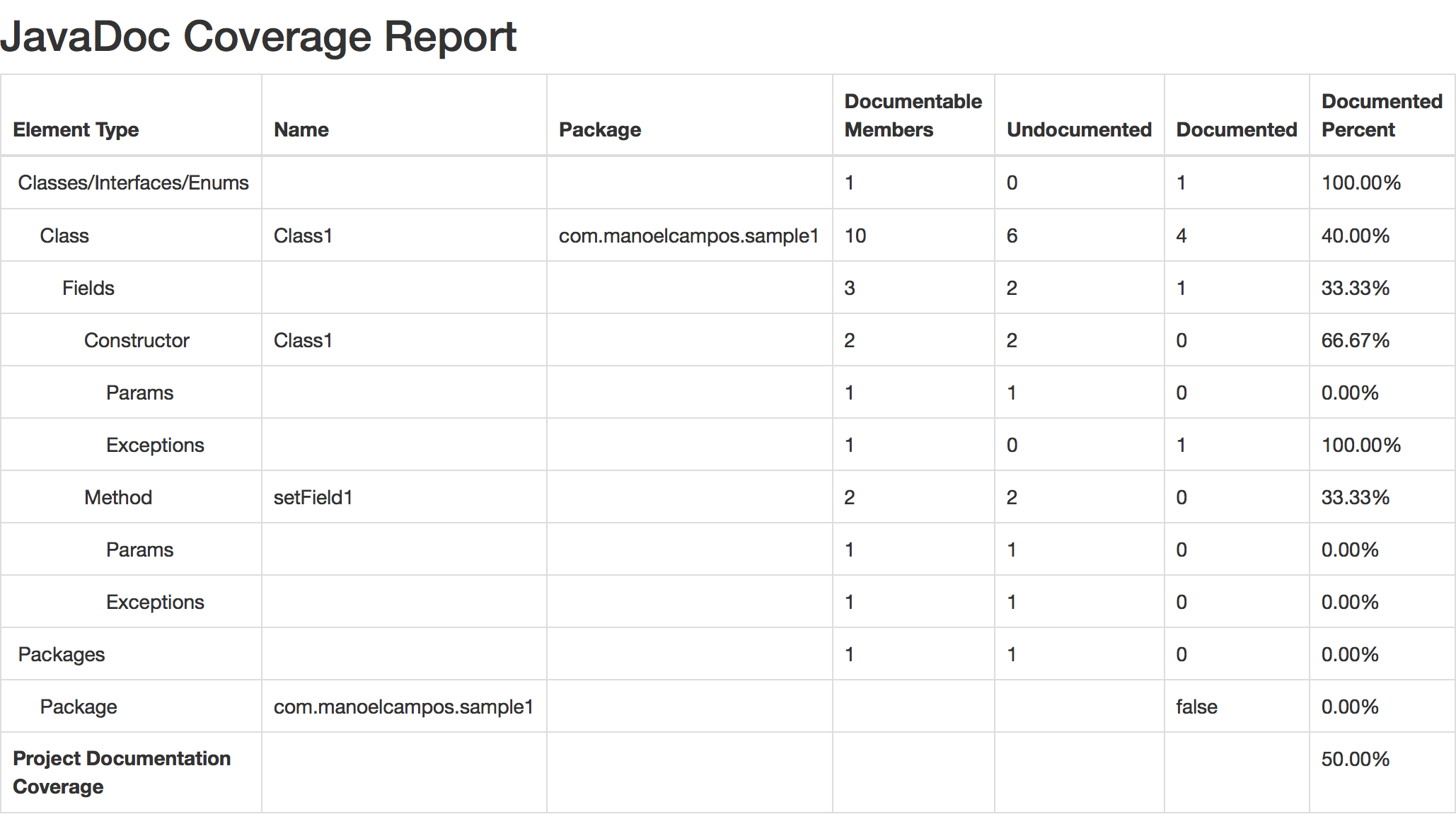
The Doclet parses java source files and checks the percentage of the Java code covered by JavaDoc documentation, including:
- packages (Java 9 modules not supported yet)
- classes, inner classes, interfaces and enums
- class attributes
- methods, parameters, exceptions and return value.
A sample coverage report is available here.
Current IDEs warn about missing JavaDoc tags and documentation, allowing you to individually fix the issues, but you don’t get a big the picture. Similar to code coverage tools, this plugin provides a way to get a summarized overview of your project’s documentation coverage. It provides a Doclet to be used with the JavaDoc Tool to show JavaDoc documentation coverage of your project.
Usage
The easier ways to use the plugin is through Maven or Gradle. You can use the plugin calling the JavaDoc Tool directly from the command line (but this isn’t handy and it isn’t explained here).
Maven: Using the CoverageDoclet in a regular way
To generate the regular JavaDoc HTML files and the coverage report, you have to include two <execution> tags for the maven-javadoc-plugin inside your project’s pom.xml file, as the exemple below:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-javadoc-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.10.4</version>
<executions>
<!-- Exports JavaDocs to regular HTML files -->
<execution>
<id>javadoc-html</id>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>javadoc</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<!-- Generates the JavaDoc coverage report -->
<execution>
<id>javadoc-coverage</id>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>javadoc</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<doclet>com.manoelcampos.javadoc.coverage.CoverageDoclet</doclet>
<docletArtifact>
<groupId>com.manoelcampos</groupId>
<artifactId>javadoc-coverage</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</docletArtifact>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugins>
<build>
Now, to generate the regular JavaDocs in HTML and the documentation coverage report, you can execute the package goal in Maven, using your IDE or the command line inside your project’s root directory:
mvn clean package
The JavaDoc coverage report is generated by default as javadoc-coverage.html at target/site/apidocs/.
There is a sample project where you can test the plugin. Just execute the command above inside the project’s directory to see the results.
Maven: Using the CoverageDoclet with the maven-site-plugin
If you are generating a maven site and want to include the regular JavaDocs HTML and the JavaDoc Coverage Report into the “Reports” section of the site, the maven-javadoc-plugin must be included with slightly different configurations into the <reporting> tag (instead of the <build> tag), as the example below:
<reporting>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-javadoc-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.10.4</version>
<reportSets>
<reportSet>
<!-- Exports JavaDocs to regular HTML files -->
<id>javadoc-html</id>
<reports>
<report>javadoc</report>
</reports>
</reportSet>
<reportSet>
<!-- Generates the JavaDoc coverage report -->
<id>javadoc-coverage</id>
<reports>
<report>javadoc</report>
</reports>
<configuration>
<name>JavaDoc Coverage</name>
<description>Percentage of the code coverage by JavaDoc documentation.</description>
<doclet>com.manoelcampos.javadoc.coverage.CoverageDoclet</doclet>
<docletArtifact>
<groupId>com.manoelcampos</groupId>
<artifactId>javadoc-coverage</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</docletArtifact>
<!-- This is the same as using -d into the additionalparam tag -->
<destDir>javadoc-coverage</destDir>
<!-- You can also use -o instead of -outputName to define
the name of the generated report. -->
<additionalparam>-outputName "index.html"</additionalparam>
</configuration>
</reportSet>
</reportSets>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</reporting>
Notice that in this case, the coverage report is being generated into the target/site/javadoc-coverage (as defined by the destDir tag) with the name of index.html (as defined by the <additionalparam> tag), as required for the maven site. More details of additional parameters is provided in the next section.
Now, to generate the site you can execute:
mvn clean site
The list of project’s reports will be included into the target/site/project-reports.html file.
Gradle
To use the Doclet with Gradle, add the following code to your build.gradle file.
configurations {
// Other configuration lines might be in here
javadocCoverage
}
dependencies {
// Your application's other dependencies go here.
javadocCoverage "com.manoelcampos:javadoc-coverage:1.1.0"
}
// This generates the Javadoc coverage report into build/reports/javadoc/javadoc-coverage.html
task javadocCoverageReport(type: Javadoc, dependsOn: javadoc) {
source = sourceSets.main.allJava
destinationDir = reporting.file("javadoc")
options.docletpath = configurations.javadocCoverage.files.asType(List)
options.doclet = "com.manoelcampos.javadoc.coverage.CoverageDoclet"
}
// Optionally you can add the dependsOn here so that when you generate the javadoc
// jar, e.g. if you include the javadocJar in a publishing configuration, the javadoc
// coverage report will be generated automatically.
task javadocJar(type: Jar, dependsOn: javadocCoverageReport) {
classifier "javadoc"
from javadoc.destinationDir
}
Additional Configuration (optional)
You can define additional configurations for the plugin. The examples below are presented only for Maven (but the same parameters work for Gradle).
Changing the name of the coverage report file
The CoverageDoclet accepts the command line parameter -outputName (-o for short) to set the name of the report. The following example shows the code to be added to the <configuration> tag of the maven-javadoc-plugin:
<additionalparam>-outputName "my-project-javadoc-coverage-report.html"</additionalparam>
Excluding packages from the coverage report
You can exclude some packages from the coverage report by adding the code example below into the <configuration> tag of the maven-javadoc-plugin.
<configuration>
<doclet>com.manoelcampos.javadoc.coverage.CoverageDoclet</doclet>
<docletArtifact>
<groupId>com.manoelcampos</groupId>
<artifactId>javadoc-coverage</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</docletArtifact>
<!-- Excludes packages from the coverage report. -->
<excludePackageNames>com.manoelcampos.sample2</excludePackageNames>
</configuration>
The example shows how to ignore the package com.manoelcampos.sample2 from the coverage report. The <excludePackageNames> tag accepts a list of packages separated by : and also wildcards such as *.
For more details, check this link.
If you are generating the regular JavaDoc HTML files, you have to include this configuration only where the CoverageDoclet is being used into your pom.xml, unless you want these packages to be excluded from the regular JavaDocs too.
Building the Doclet from Sources
The Doclet is a Java Maven project which can be built directly from any IDE or using the following maven command:
mvn clean install
The command builds the Doclet and install it at your local maven repository.
